Minimally invasive surgery can mean smaller incisional approaches or endoscopic procedures. Using minimally invasive techniques and surgeries provide our patients with many benefits over traditional treatments and surgeries. These benefits typically include:
- Significantly less pain over traditional surgery
- Quicker recovery time
- Faster return to work and normal activities
- Less damage to tissue
- Less scarring
- Outpatient surgery
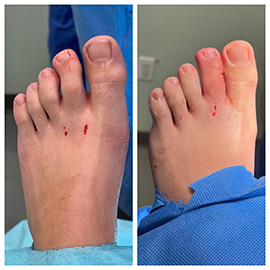
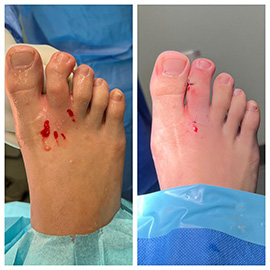
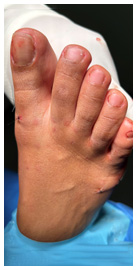
Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery. This type of procedure requires only micro incisions to be made in the skin of the foot to correct the deformity and realign the bones. This type of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is an alternative to traditional bunion surgery. It can reduce the pain, risk, recovery time and scarring associated with open surgery. There are various techniques of MIS bunion surgery including Percutaneous Chevron Akin-where the podiatrist cuts and repositions the first metatarsal and big toe bones-and minimally invasive Percutaneous Lapidus technique, which involves cutting the big toe bone, then realigning and fusing the midfoot joint.
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy (EPF) is a minimally invasive, endoscopic technique used to release extreme tension of the plantar fascia. An endoscope provides clear visualization of the inferior surface of the plantar fascia, allowing the surgeon to release tension in the medial band. Following the procedure, a sterile dressing is worn for approximately 3-5 days, then the patient is generally allowed to wear comfortable shoes as tolerated.
Endoscopic Gastrocnemius Recession (EGR) is a minimally invasive technique designed for gastrocnemius equinus treatment. Equinus is a limitation of ankle joint motion. The bi-portal approach, using a scope which provides clear visualization for safe division of the fascia of the gastrocnemius (calf) muscle. The sheath of the scope protects the sural nerve from injury. Once adequate release is attained, all equipment is removed. The skin is closed with sutures. Post-operative management is dependent upon other procedures performed in conjunction with the EGR technique.
Subtalar Joint Arthroereisis is a minimally invasive flat foot surgery. It is a less aggressive option used to treat a mild or pediatric flatfoot. The implant blocks excessive pronation of the subtalar joint. A small incision is made over the lateral foot, and then a small implant is inserted into the sinus tarsi, a small canal that goes up to the ankle below the talus bone. Minimal dissection allows for a quicker recovery period and a shorter immobilization time when compared to full reconstructive methods.